There are panels that are used to collect the sun’s energy. Once the initial energy is collected it is then sent to a solar inverter which then sends the power to a battery inverter.
From there it will use energy to power electronics that are in your home. In the end, whatever green energy is created and is not used goes to the battery bank. This is a personal battery that saves power for the home to use at night or on days that are cloudy and overcast.
It can minimize carbon footprint, just like any other renewable energy sources (like wind turbines, geothermal power sources, and many others).
This system will help you save on electricity costs.
The off-grid solar system design can act as a storage for energy (like batteries) to be later used as backup power for houses.
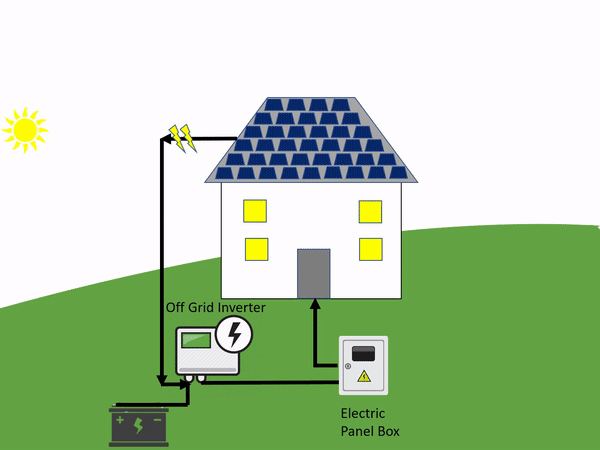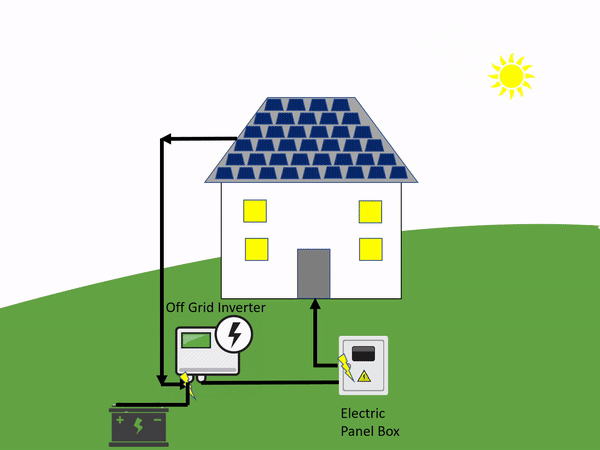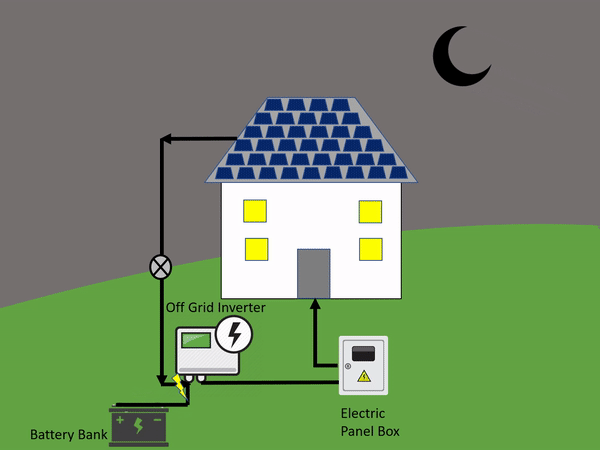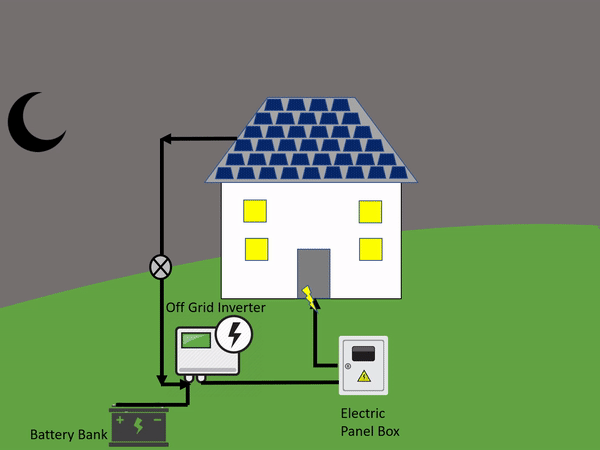
The off-grid systems rely on a battery to save all the power created just for that one household or building. An on-grid solar system is the opposite.
Any power that is created by that home or buildings solar panels is sent to an electricity grid where anyone who is also connected to that same grid can use that energy.
Put simply, grid-tied is a solar system tied in with the grid and in most provinces that offer credit to residential and business customers who are making excess electricity with their solar panel systems and sending it back to the grid.
Grid-Tied can save homeowners thousands of rands on their utility bills every year, so it’s a good reason to make the money saving choice and go solar sooner rather than later.
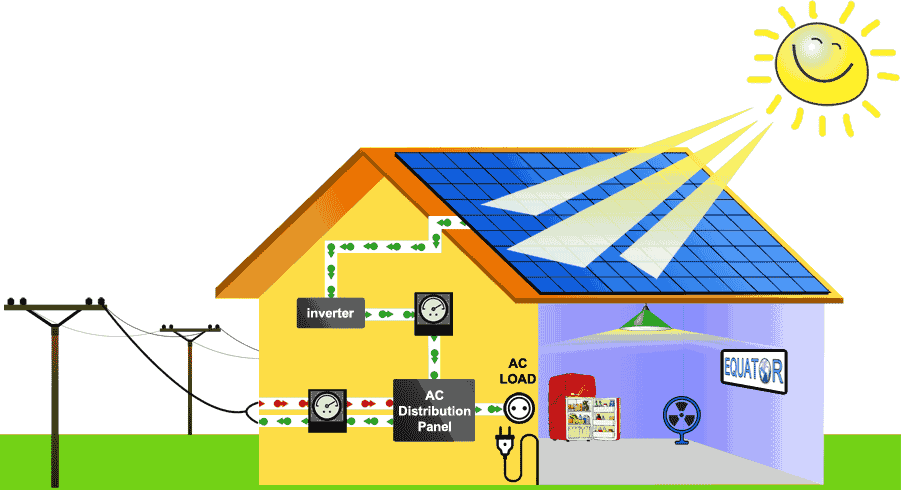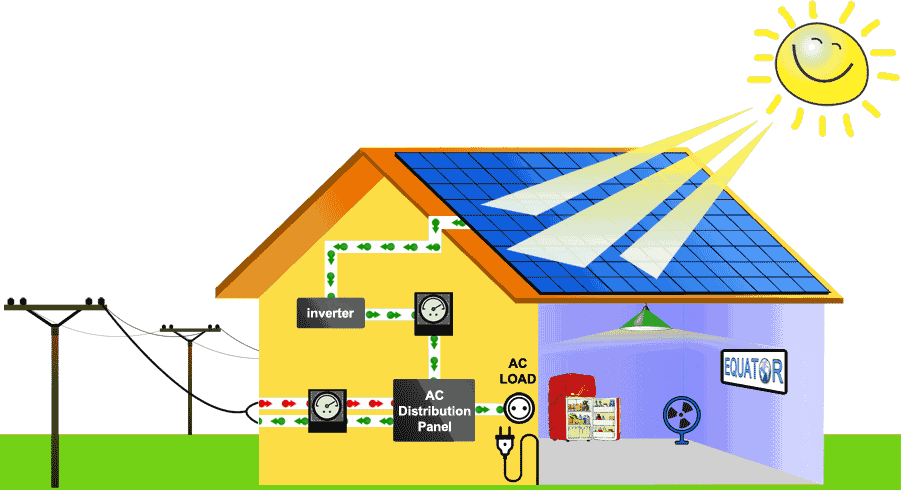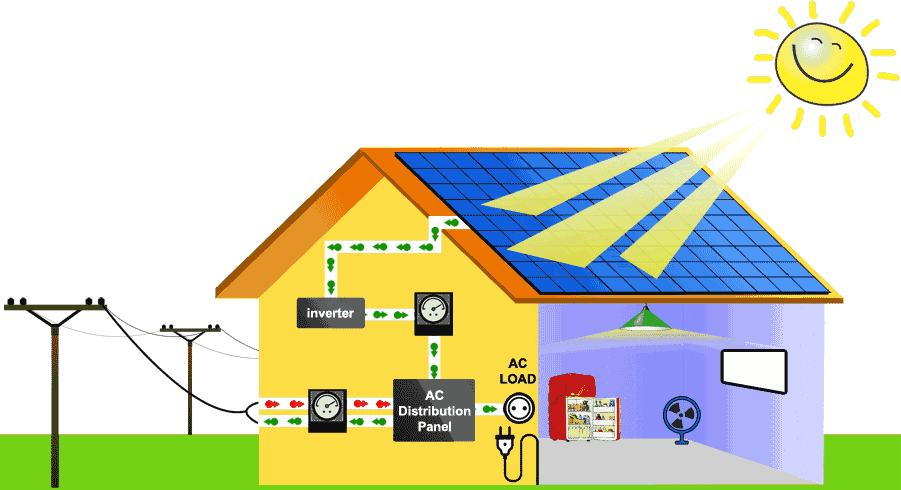
When you have a rooftop solar system, it can often generate more electricity than you consume during daylight hours.
With a grid-tied system, the homeowner has the option of sending electricity back to the grid.
When your house or business is grid-tied, you may get a credit to hedge against the electricity you use from the grid when it’s not sunny or at nighttime. The excess energy generated gets put back to the grid.
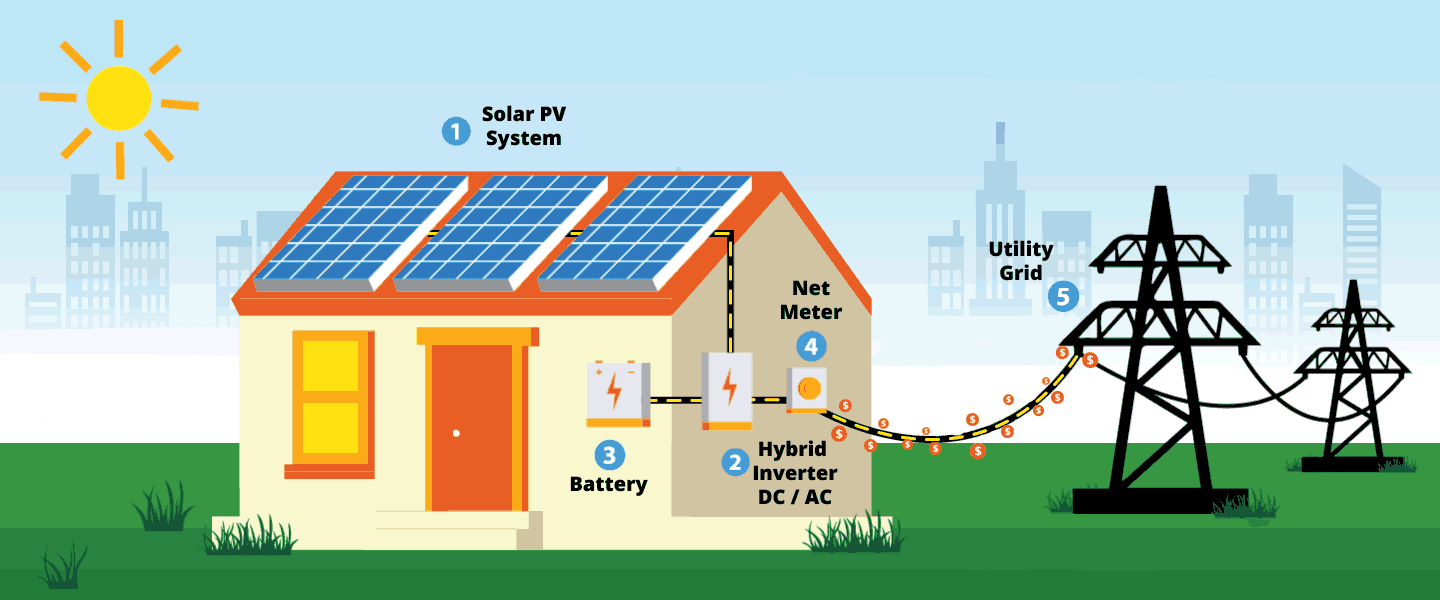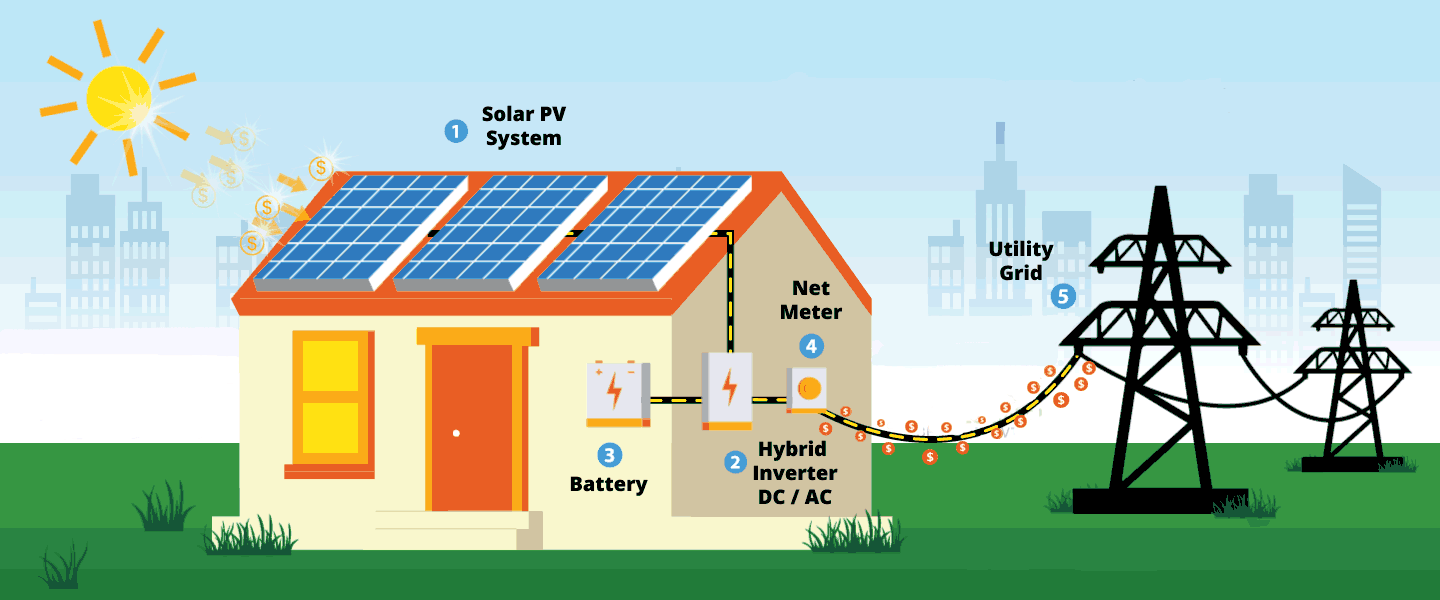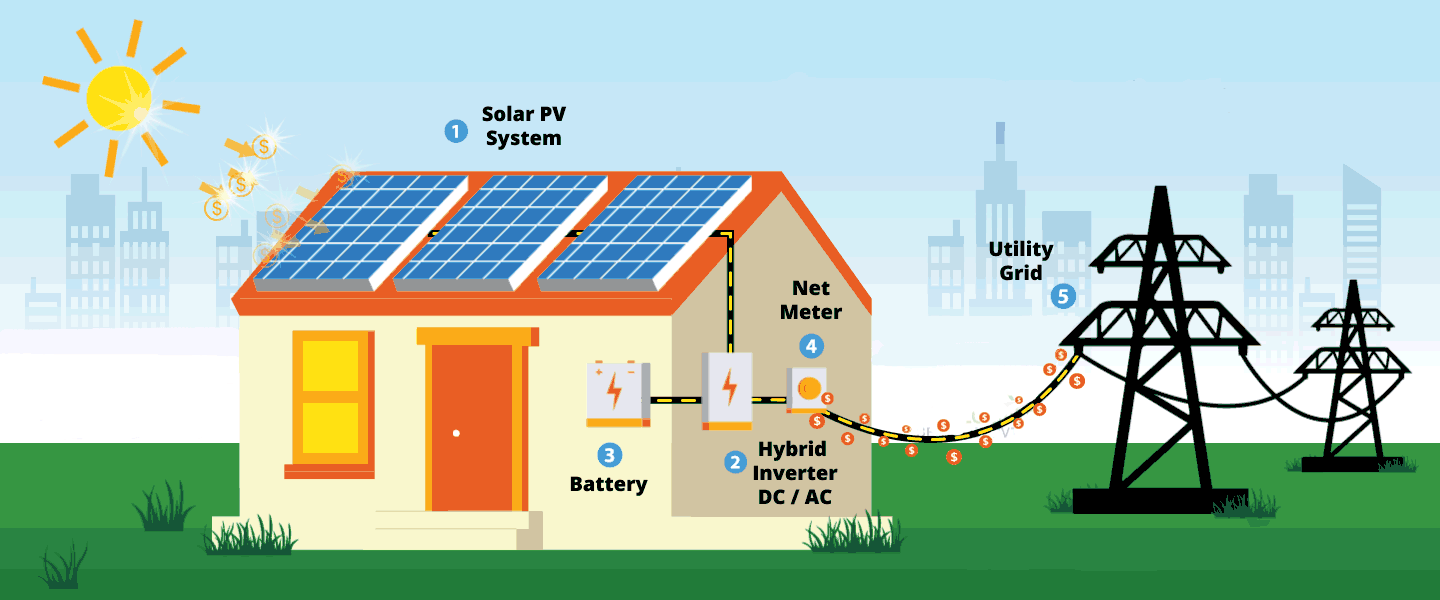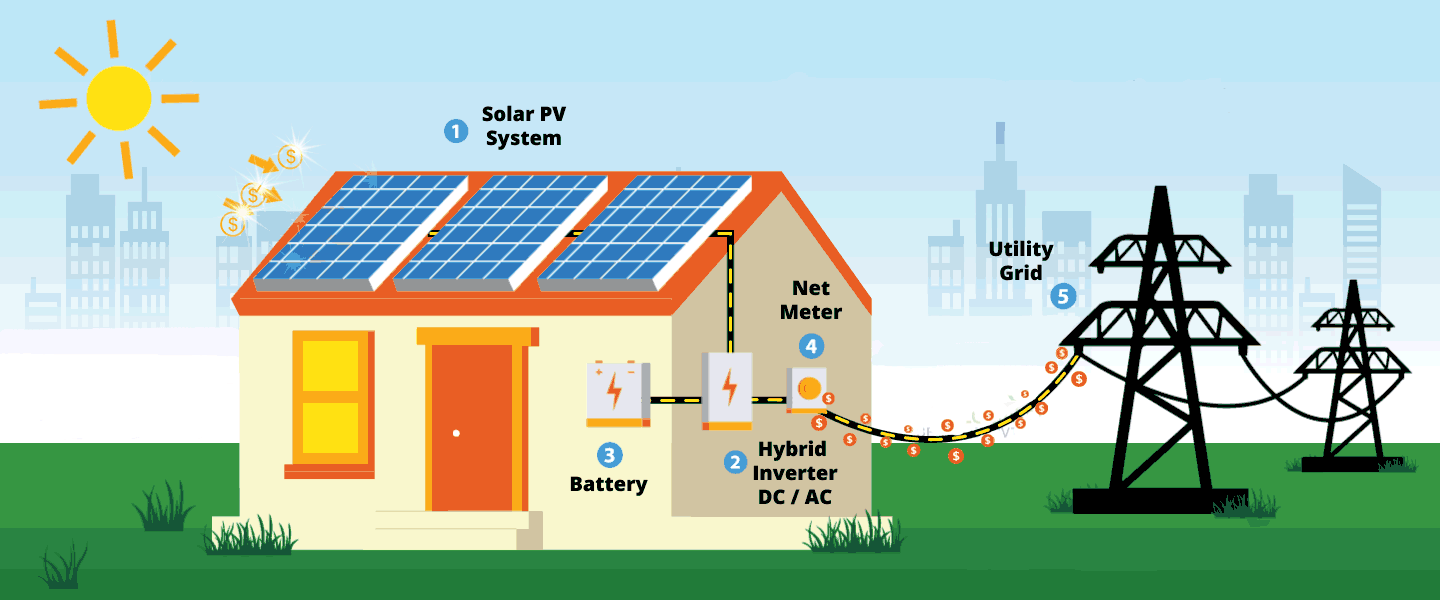
Hybrid solar systems combine the best from grid-tied and off-grid solar systems. It can either be described as off-grid solar with utility backup power, or grid-tied solar with extra battery storage.
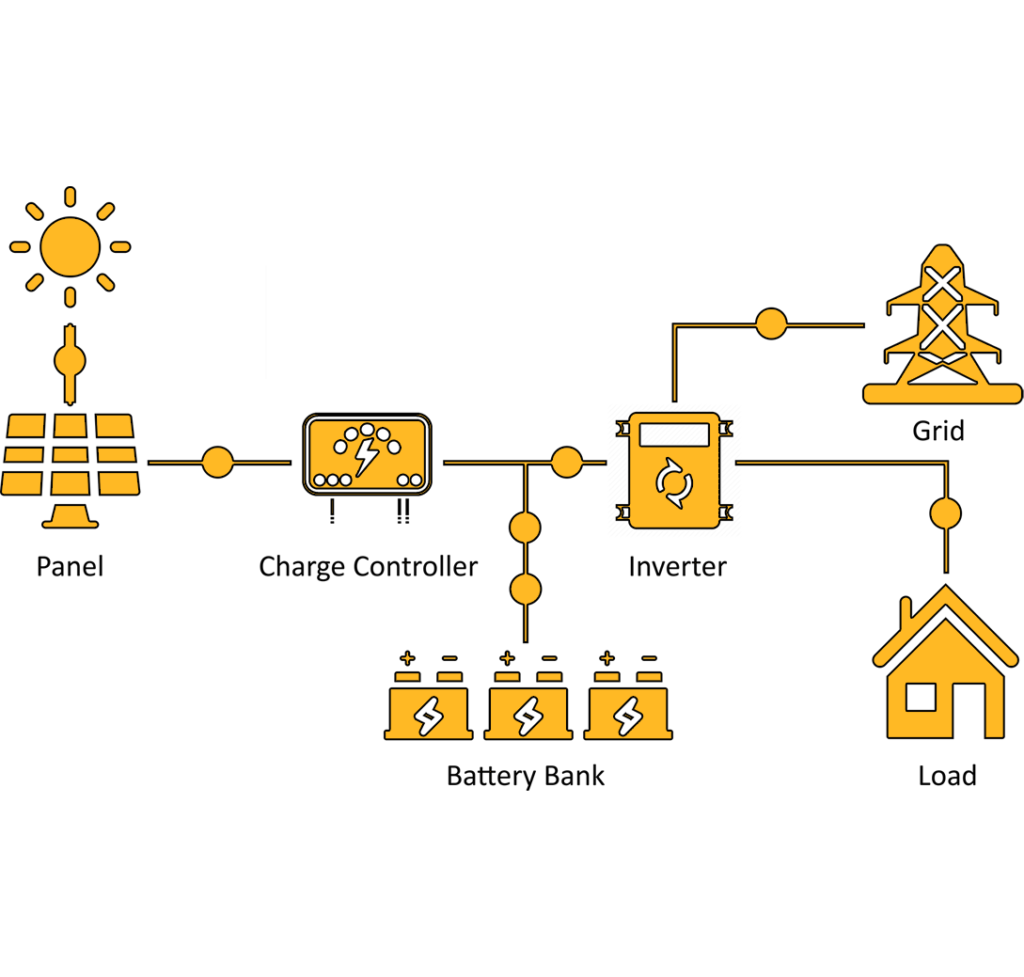
PV panels
Charge Controller
Battery Bank
DC Disconnect (additional)
Battery-Based Grid-Tie Inverter
Power Meter
An off-grid system is not connected to the electricity grid and therefore requires battery storage.
An off-grid solar system must be designed appropriately so that it will generate enough power throughout the year and have enough battery capacity to meet the home’s requirements, even in the depths of winter when there is less sunlight.
Independence from spiraling diesel generator costs
Independence from outrageous utility costs
Reliable and scalable off-grid solution
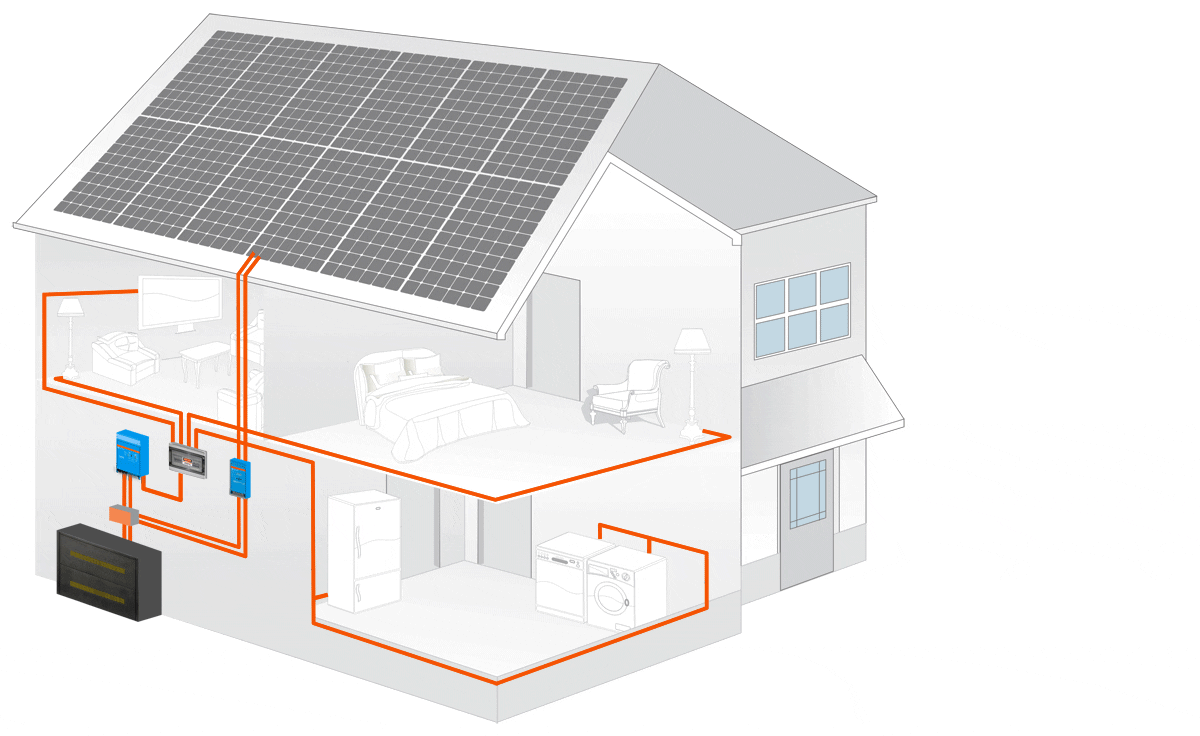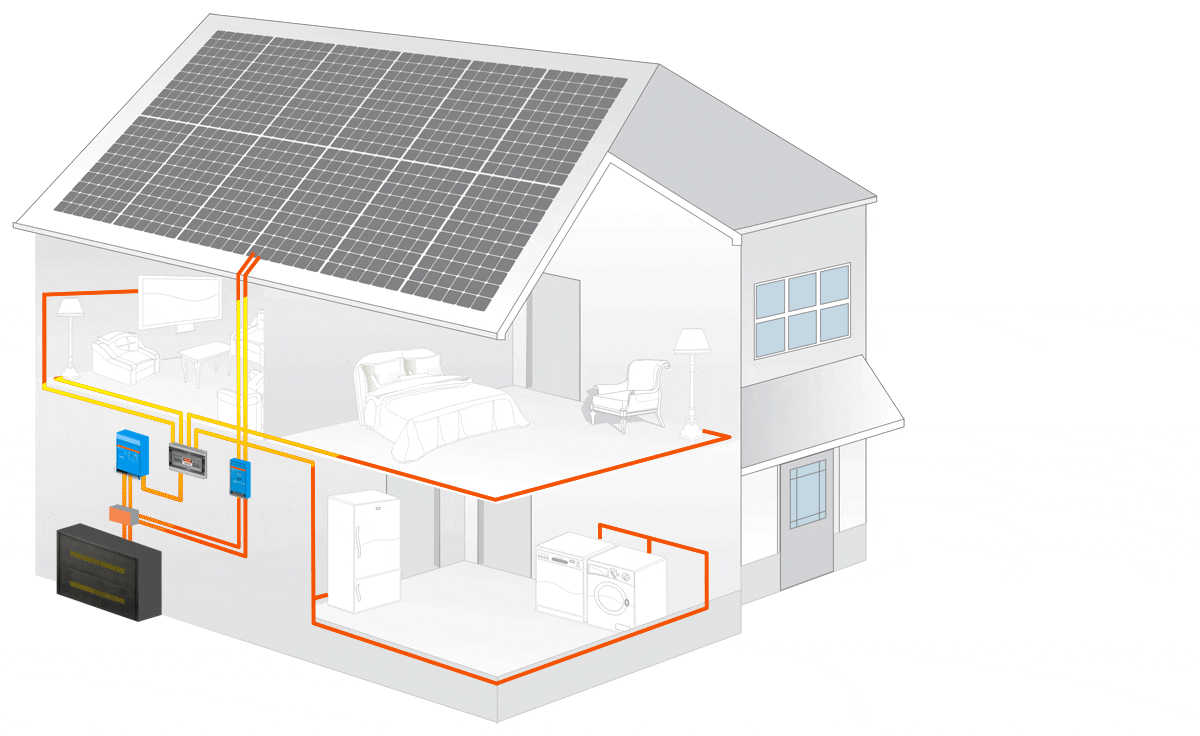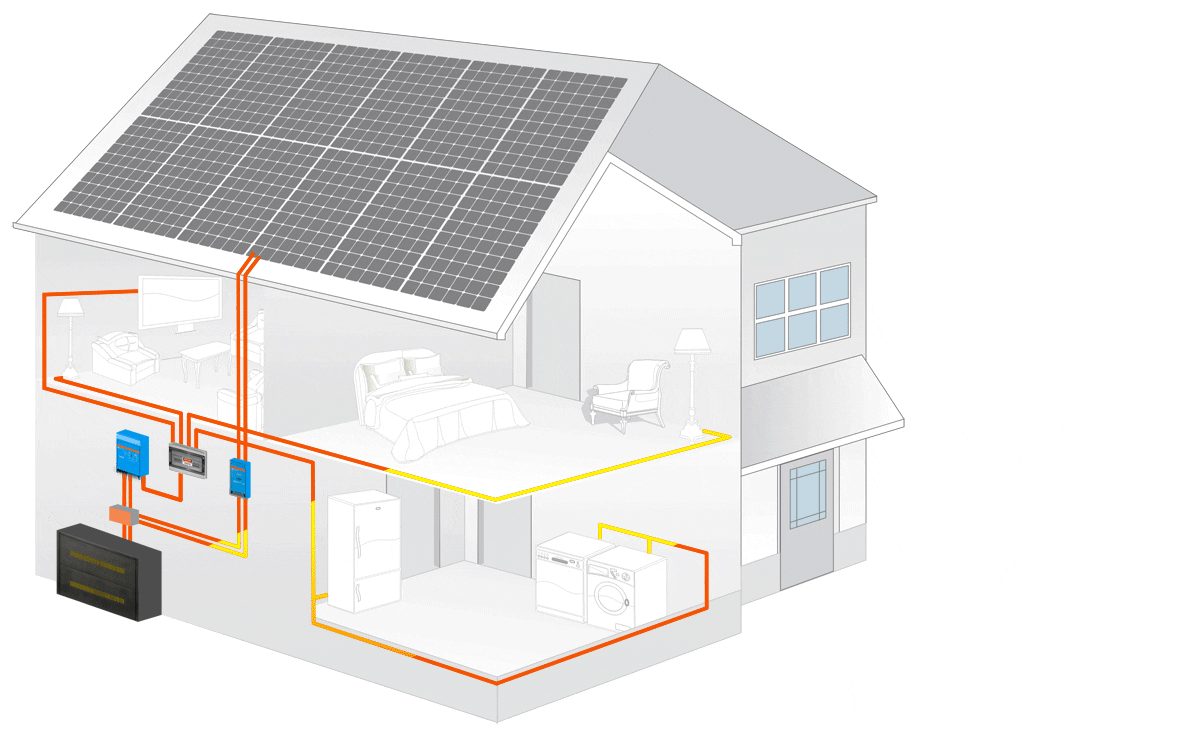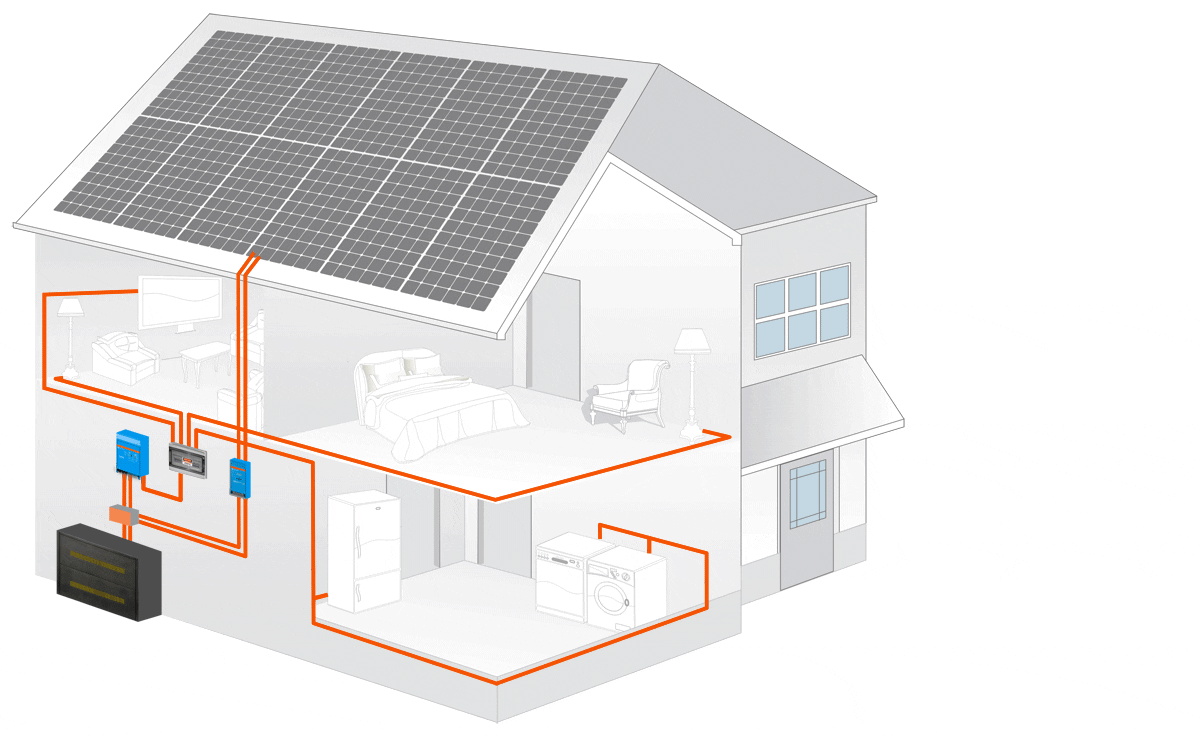
An off-grid solar system uses the basic principles of solar power. When we say this, we simply mean that with this system there are panels that are used to collect the sun’s energy. Once the initial energy is collected it is then sent to a solar inverter which then sends the power to the battery storage system.
From there it will use energy to power electronics that are in your home. In the end, whatever green energy is created and is not used goes to the battery bank. This is a personal battery that saves power for the home to use at night or on days that are cloudy and overcast.

Put simply, grid-tied is a solar system tied in with the grid and in most provinces that offer credit to residential and business customers who are making excess electricity with their solar panel systems and sending it back to the grid.
Grid-Tied can save homeowners thousands of rands on their utility bills every year, so it’s a good reason to make the money saving choice and go solar sooner rather than later.

When you have a rooftop solar system, it can often generate more electricity than you consume during daylight hours.
With a grid-tied system, the homeowner has the option of sending electricity back to the grid.
When your house or business is grid-tied, you may get a credit to hedge against the electricity you use from the grid when it’s not sunny or at nighttime. The excess energy generated gets put back to the grid.